Data Structures: Stack
Intro
Stack is a data structure and it is widely used and not known in the same time. Language runtimes, like JVM and .NET Runtime (including Core) use it, but you also can find it in NodeJS, and many other places. It is a perfect data structure controlling the execution order of the code. However, on daily basis you might not use it as frequently like like arrays or lists.
Stack
A stack is a collection on elements put on each other. The screenshot below shows a stack. The left side the accessibility order of the elements are displayed.
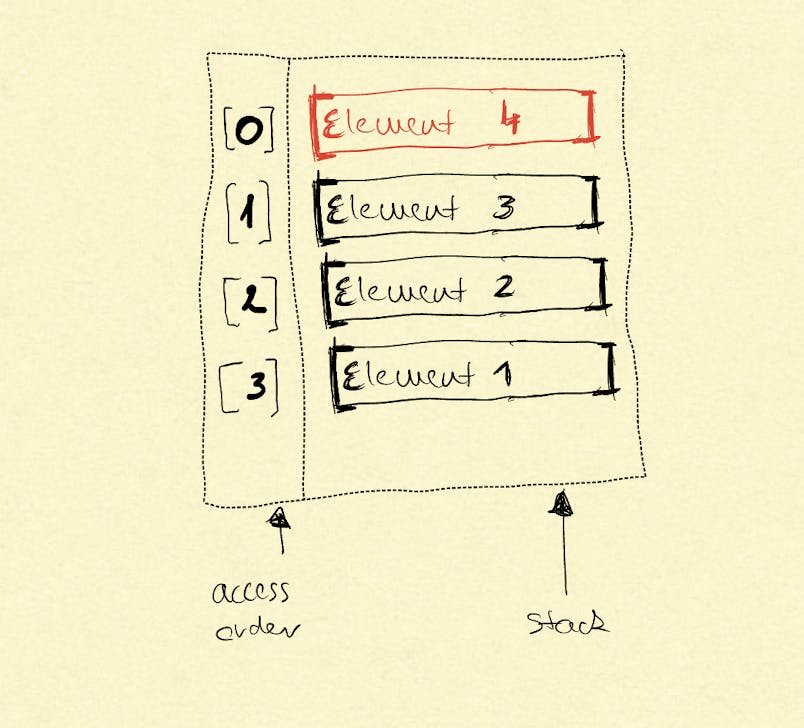
Operations
Stacks have two main operations: push and pop. Push adds an element on the top of the stack while pop removes the top element from the stack. There are two main rules when it comes to stacks:
- you can add (push) an element only to the top of the stack
- you can remove (pop) only the top element of the stack
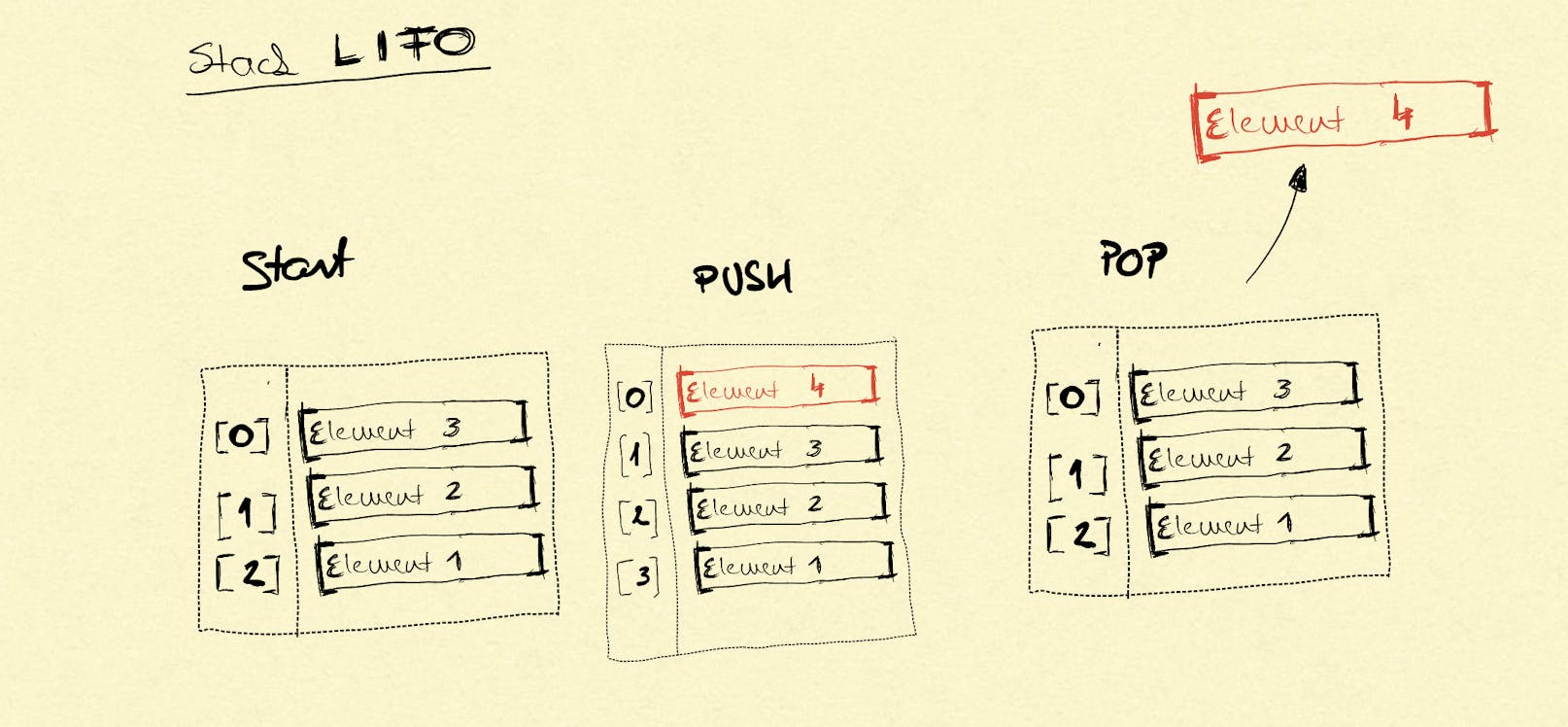
LIFO
These rules describe the LIFO behaviour, meaning Last In First Out. LIFO means that the last element added to the stack (push) will be the first element can be removed (pop).
The screenshot below displays how LIFO works in a very schematic way. Start, we have a stack where the "Element 3" is the top element. In the Push step we add "Element 4", which became the first element available, and the stack size grows to 4. When the stack is Popped then "Element 4" will be removed from the stack.
Complexity
Stacks can be implemented by using arrays or linked lists. In the following sections we are going to take a look at both.
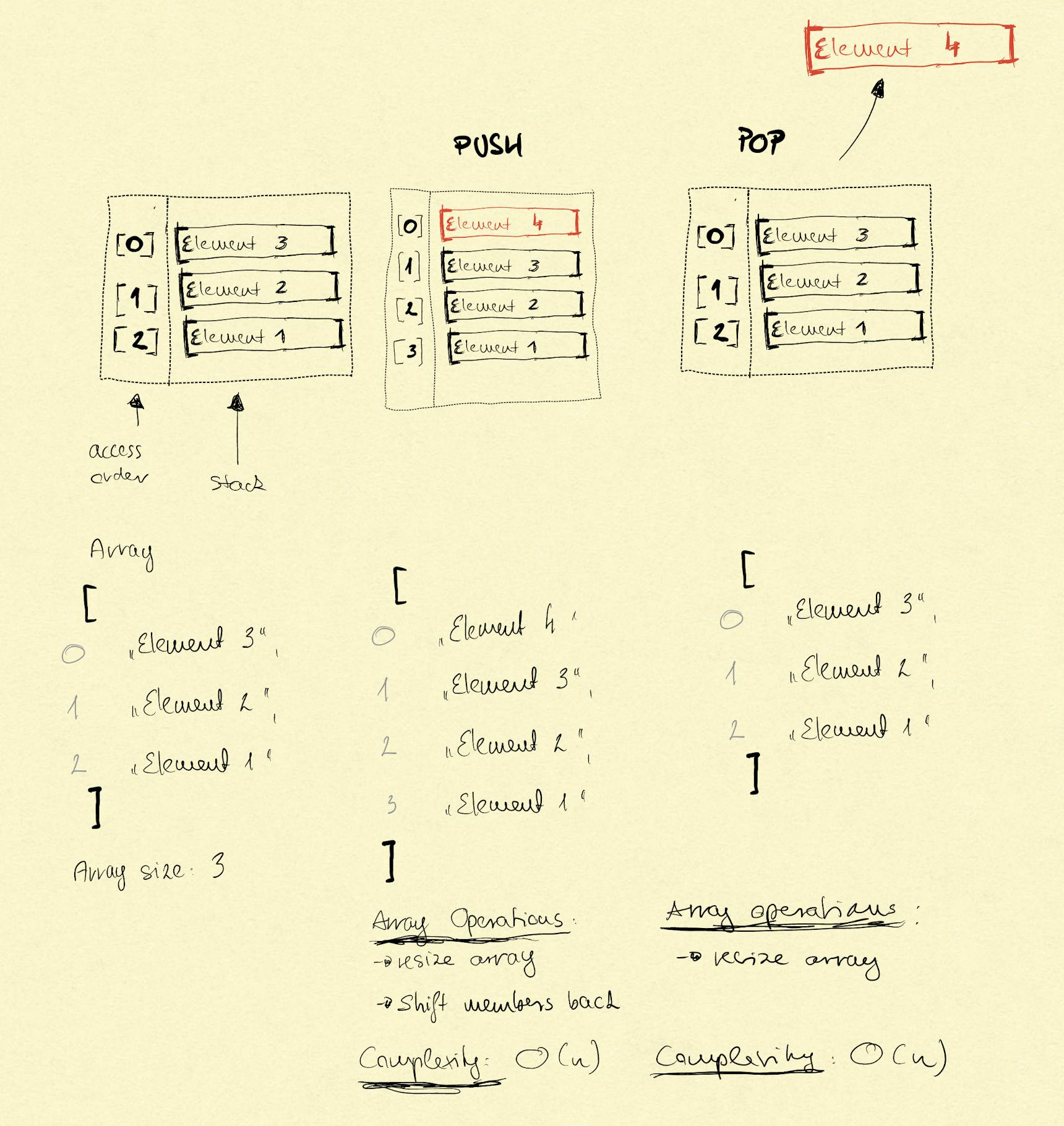
Array implementation
When stack implementation is based on arrays the size of the array is actively managed. We already know that size management is a bit problematic part of dynamic size arrays. I'm not going to include how particular languages implement array or linked list, or what dynamic size array they provide. All of these are implementation details. Knowing how data structure conceptually works helps you to ask questions how a particular language implements it.
When we push a new element to the stack then the underlying array size must be increased. Size increase is an O(n) operation. When an element is popped then the underlying array size should be decreased.
The question whether the inserted element should be the first element of an array (index 0) or the last one is again an implementation detail. When and how the array size management happens is also an implementation detail. It worth another article.
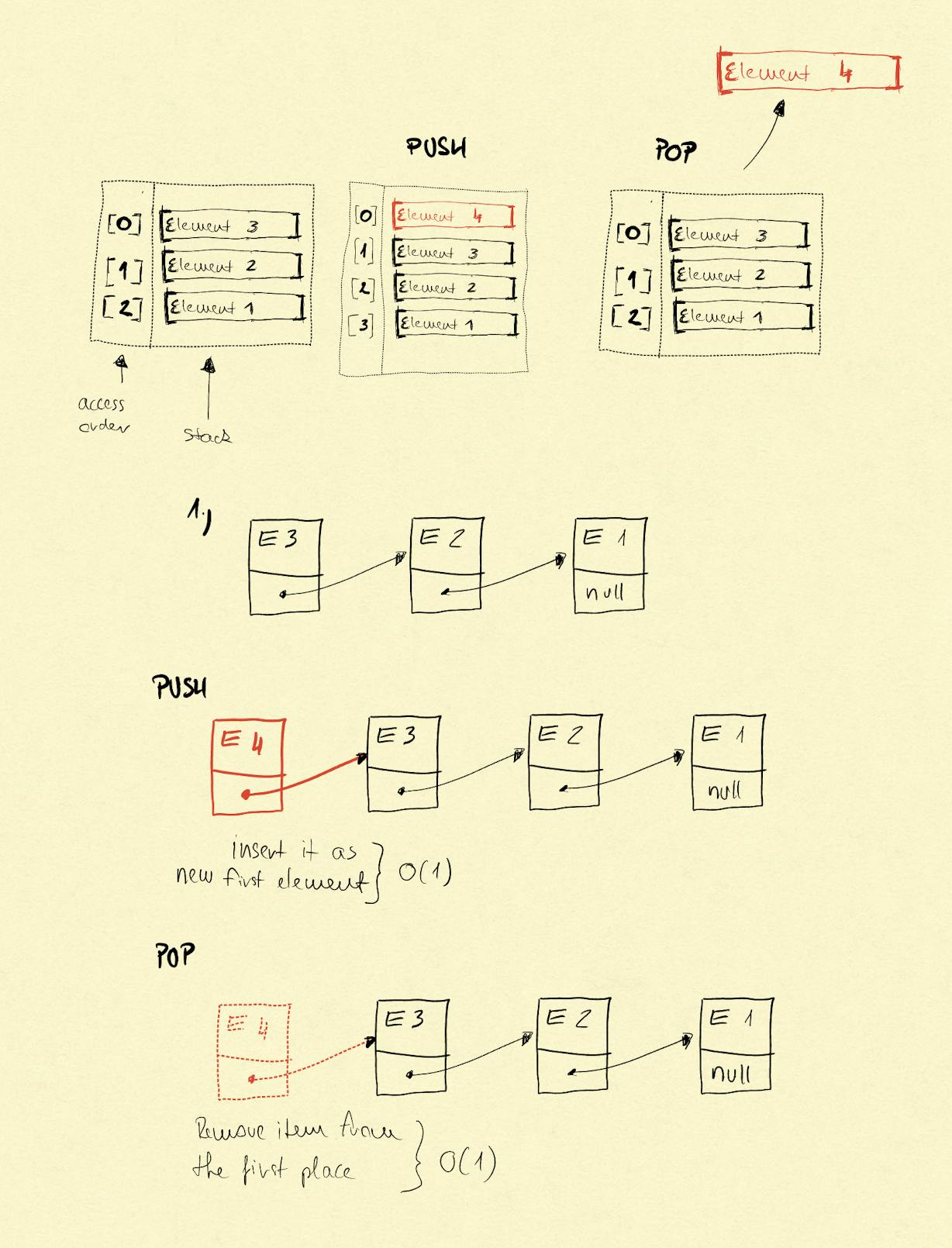
Linked list implementation
When stack is implemented by a linked list we can leverage on its O(1) operations related to its size management.
Sources
- Stack — Wikipedia
- Data Structures and Algorithms: The Complete Masterclass
- Algorithms, Fourth Edition
- Algorithms: 24-part Lecture Series
Summary
We learned what is the stack data structure, its time complexity details. For further reading you can find the links above.
Feedback
If you have any feedback, please make a comment so I'll know how I can make better these articles.
