Data Structures: The Queue
Intro
Queue is another well known and barely known data structure. Possibly you won't use it on daily basis, however you will use services built on it like a message queue.
Queue
Imagine a tube which has two ends. You put balls at one end of it and they fall out at the other end of it. The order of the balls in the tube are defined by the order they were being added. Only one element can be added, and only one element can be removed.
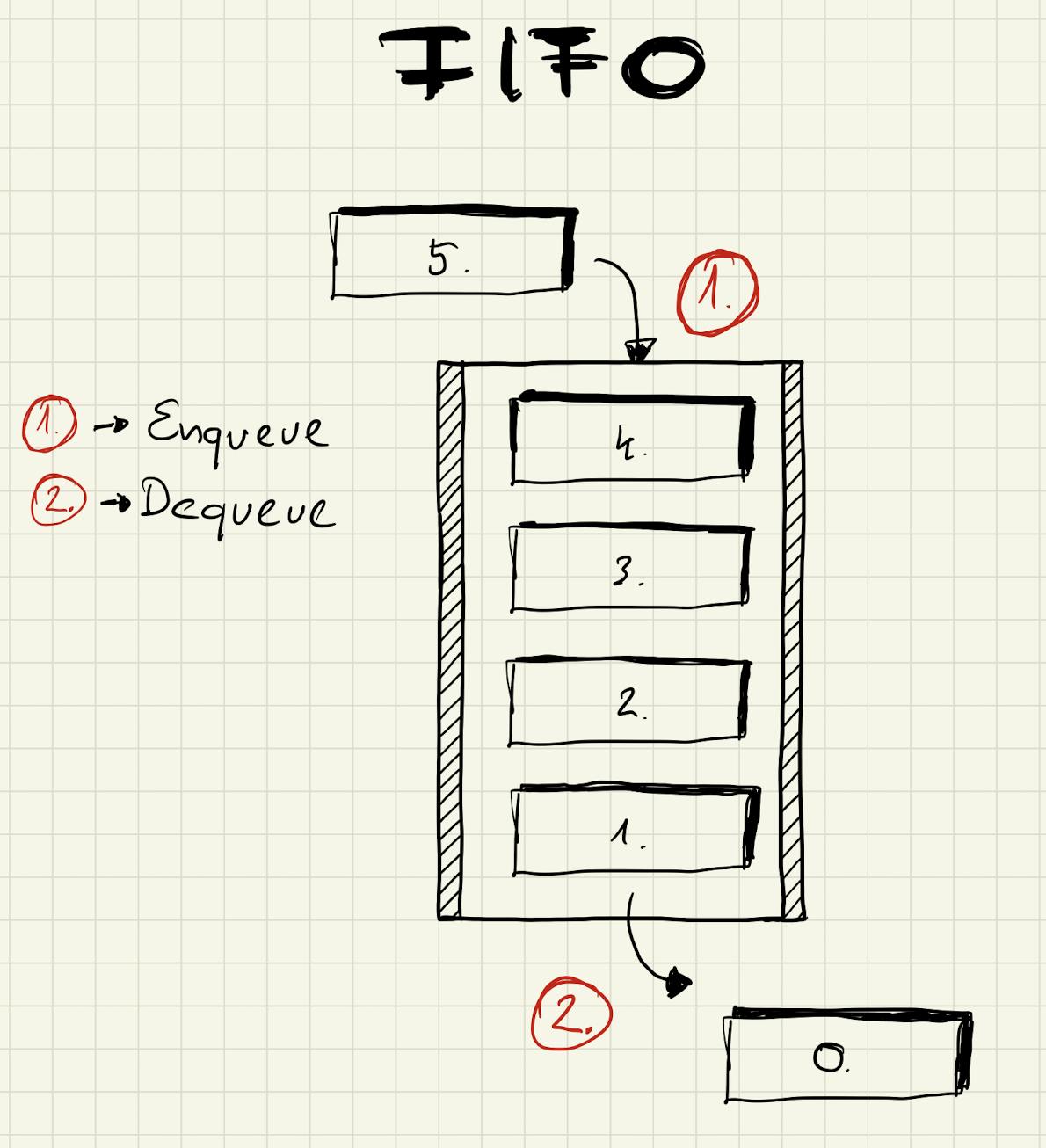
FIFO
What I described in the previous section is the FIFO way of working. It means First In First Out. The removing order of elements is exactly the same as they were being added.
Operations
A queue has two operations (it might have more depending on implementation):
- Enqueue: adding an element to the queue
- Dequeue: removing the next element from the queue
Time Complexity
The table below shows that enqueue and dequeue are O(1) operations, however it depends on the implementation.
| Operation | Time Complexity |
| Enqueue | O(1) |
| Dequeue | O(1) |
Implementations
Important to note that I describe a conceptual working of a queue using array or linked list. It doesn't include any implementation detail. This is something the engineer have to figure out using the language reference.
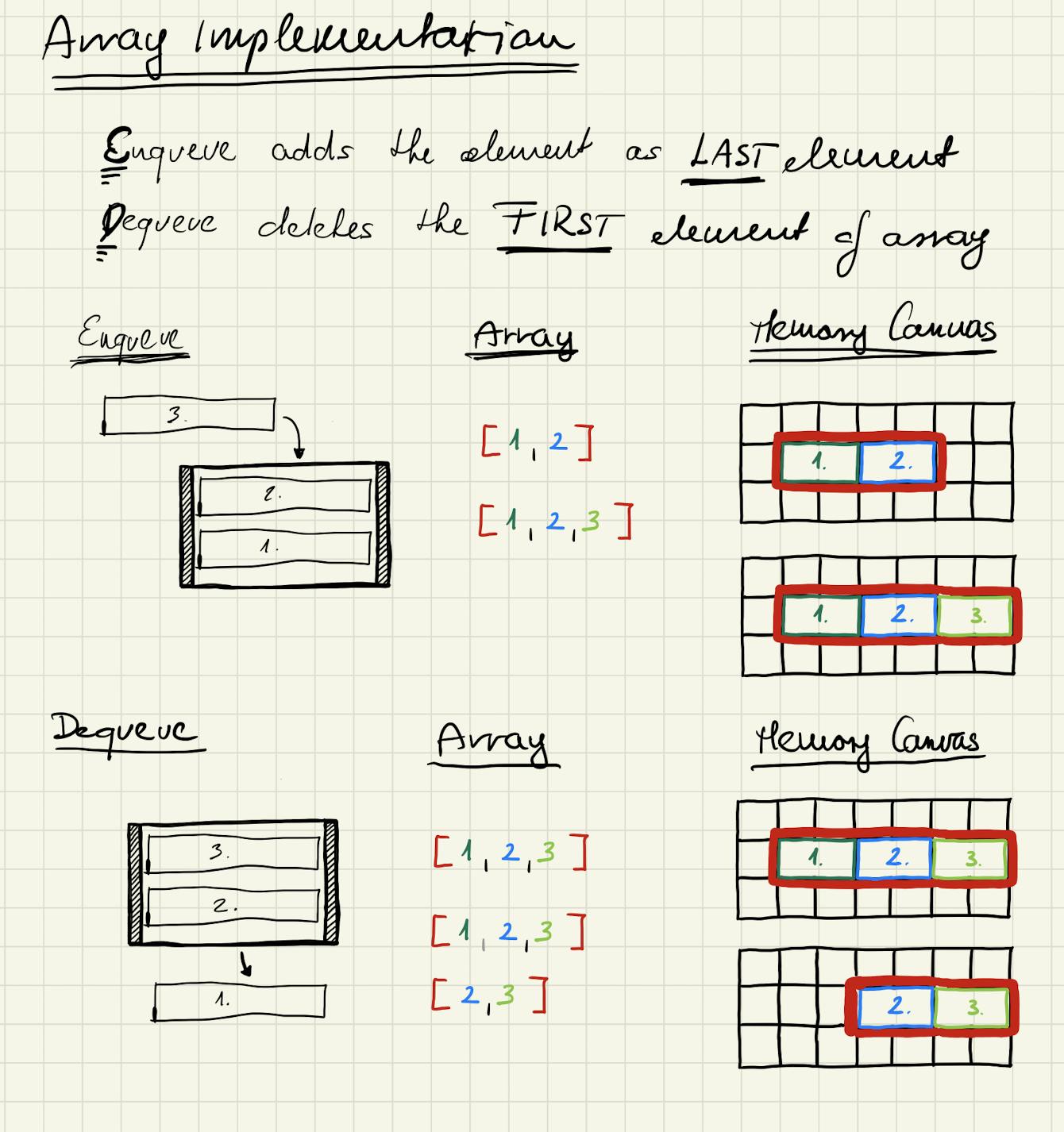
Array implementation time complexity
When array is used to implement a queue the array size has to be constantly managed. Size management is not the strongest suite of arrays as it is O(n) operation.
When an element is enqueued the underlying array size needs to be increased. When an element is dequeued the underlying array size needs to be decreased.
How these operations happen in a certain language implementation is an implementation detail.
In the picture below I also included some implementation detail. Feel free to ignore it.
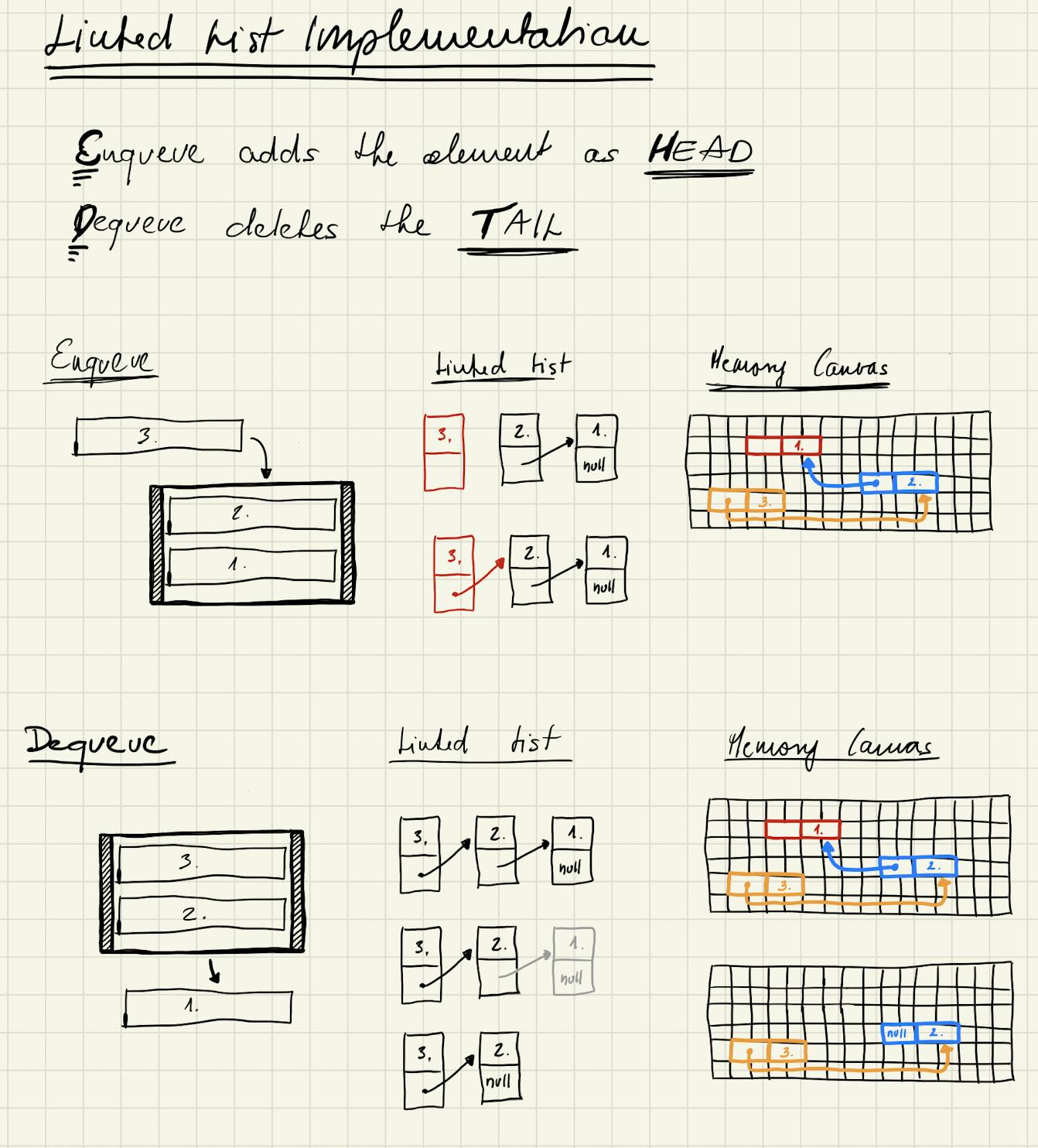
Linked List implementation time complexity
The size management of the story is the same when the queue is implemented by linked list. The only difference is that time complexity of linked list size management is O(1).
When an element is enqueued the underlying linked list size increases, and when an element is dequeued the underlying linked list size decreases.
Again, how these operations look like in a certain language implementation is an implementation detail.
Sources
- Queue — Wikipedia
- Data Structures and Algorithms: The Complete Masterclass
- Algorithms, Fourth Edition
- Algorithms: 24-part Lecture Series
Summary
We learned what is the queue data structure, its time complexity details. For further reading you can find the links above.
Feedback
If you have any feedback, please make a comment so I'll know how I can make better these articles.
